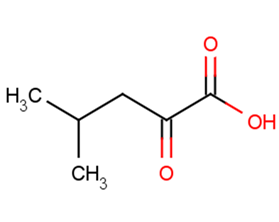
4-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid
CAS No. 816-66-0
4-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid( 4-Methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid )
Catalog No. M19851 CAS No. 816-66-0
4-Methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid is an abnormal metabolite that arises from the incomplete breakdown of branched-chain amino acids. It is both a neurotoxin and a metabotoxin.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 100MG | 48 | In Stock |


|
| 200MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 500MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product Name4-Methyl-2-oxovaleric acid
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief Description4-Methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid is an abnormal metabolite that arises from the incomplete breakdown of branched-chain amino acids. It is both a neurotoxin and a metabotoxin.
-
Description4-Methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid is an abnormal metabolite that arises from the incomplete breakdown of branched-chain amino acids. It is both a neurotoxin and a metabotoxin.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms4-Methyl-2-oxopentanoic acid
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number816-66-0
-
Formula Weight130.14
-
Molecular FormulaC6H10O3
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO: 10 mM
-
SMILESCC(C)CC(=O)C(O)=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Yudkoff M et al. Brain amino acid requirements and toxicity: the example of leucine. J Nutr. 2005 Jun;135(6 Suppl):1531S-8S.
molnova catalog



related products
-
Copper probe CF4
Copper probe CF4 (Copper fluor CF4) is a fluorescent copper probe that can be used to study colon cancer.
-
Reactive Blue 4
Reactive Blue 4 is an anthraquinone dye with phytotoxic, cytotoxic, and genotoxic.
-
Phenylalanylalanine
Phenylalanylalanine (H-Phe-Ala-OH) is a dipeptide composed of phenylalanine and alanine. Phenylalanylalanine is an incomplete breakdown product of protein digestion or protein catabolism.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


